7 Nutrient-Packed Foods to Elevate Your Brain Health
Over the past 70 years, our understanding of how diet influences mental health and disease has significantly evolved.
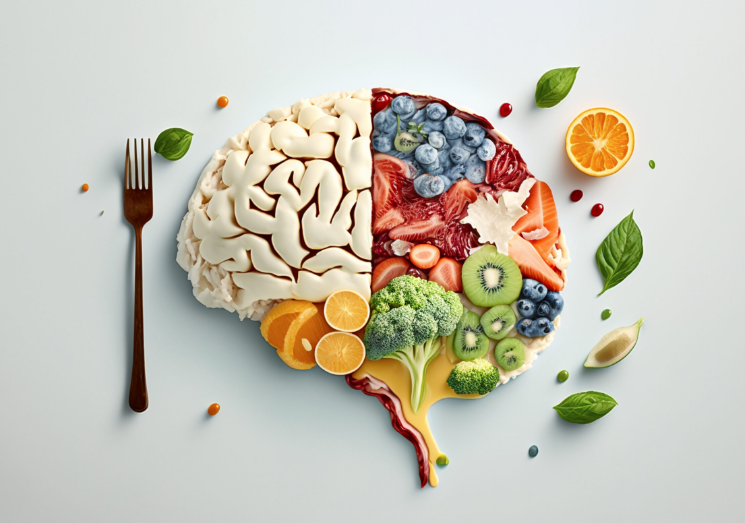
Increasing evidence demonstrates that our dietary choices have a profound impact on our mental well-being.
Now more than ever, we have the opportunity to enrich our diets with foods that are beneficial for our brain. Here are some top “power player” foods known to enhance mental health:
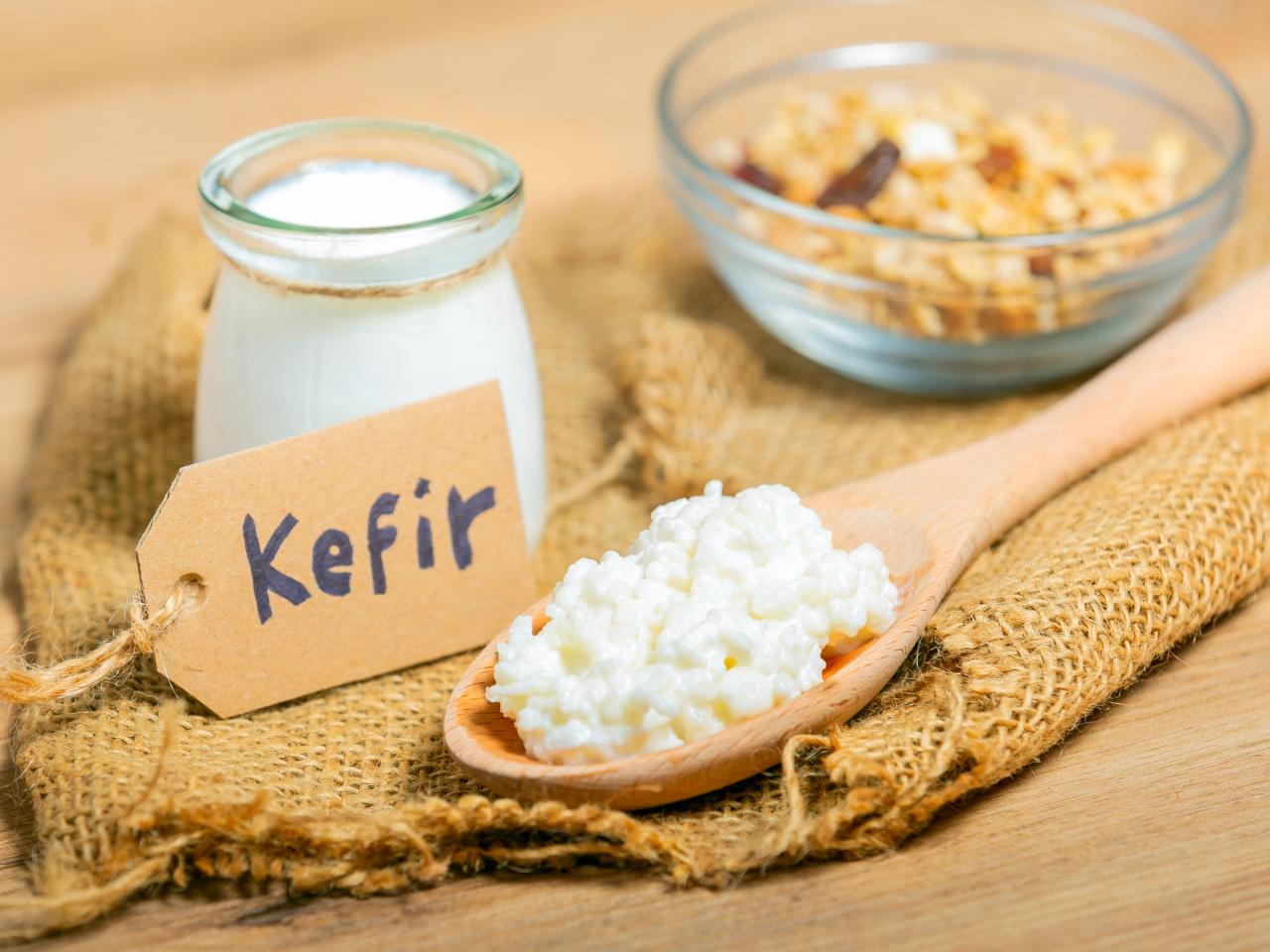
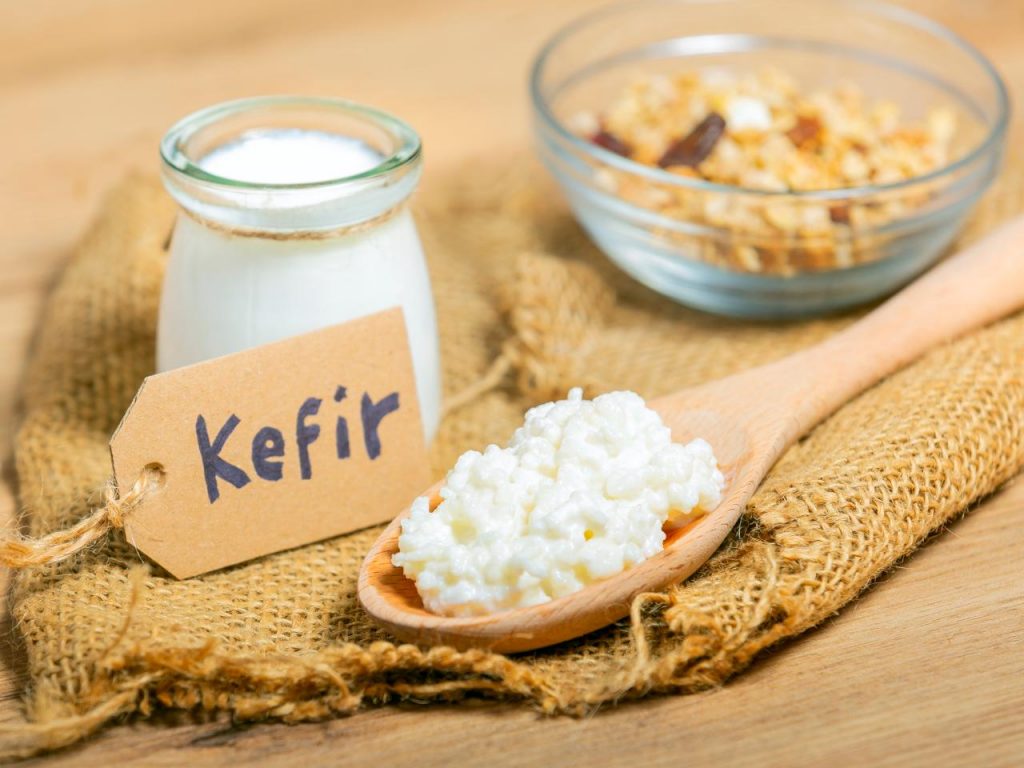
- Kefir
Kefir, a fermented dairy product, is low in lactose and rich in compounds that support both brain and gut health. Fermented foods like kefir increase microbiome diversity, which in turn supports brain health through the gut-brain axis. Research on psychobiotics—probiotics that benefit the brain—indicates that kefir can enhance cognitive functions and slow memory decline associated with aging. Try adding a tangy splash of kefir to your smoothies or salad dressings.
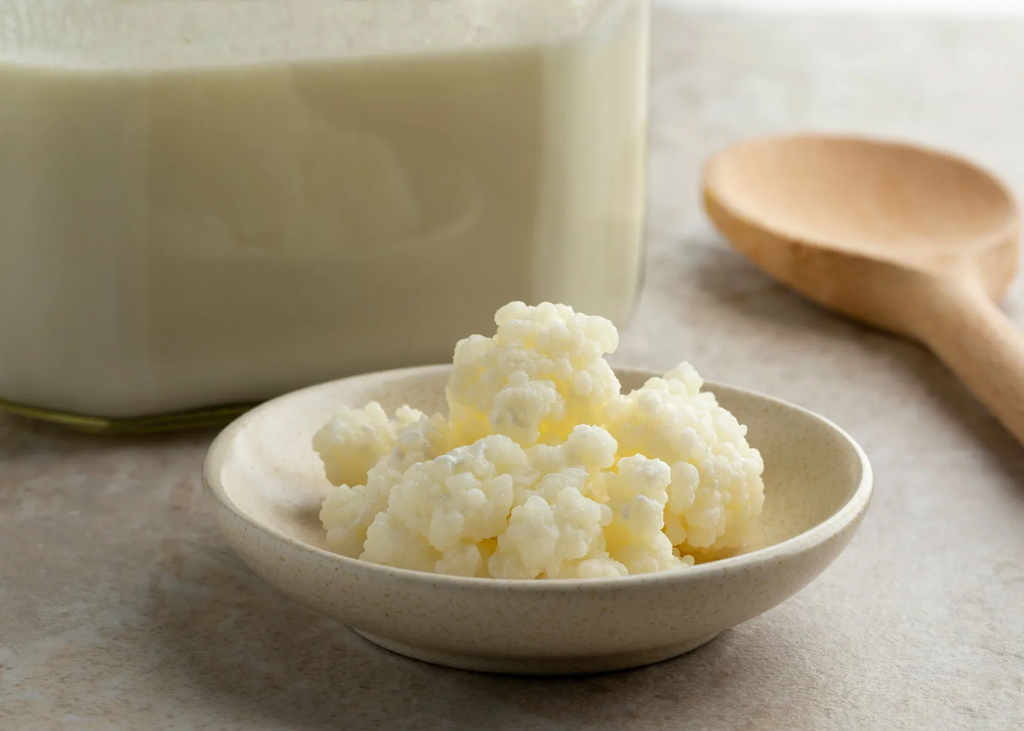

- Anchovies & Mussels
While salmon and tuna are excellent choices, expanding your seafood selection can offer additional mental health benefits. Smaller fish like mussels and anchovies contain lower levels of mercury and other pollutants, yet are rich in brain-boosting omega-3 fatty acids. Choosing smaller, tinned fish is also more economical and environmentally sustainable.

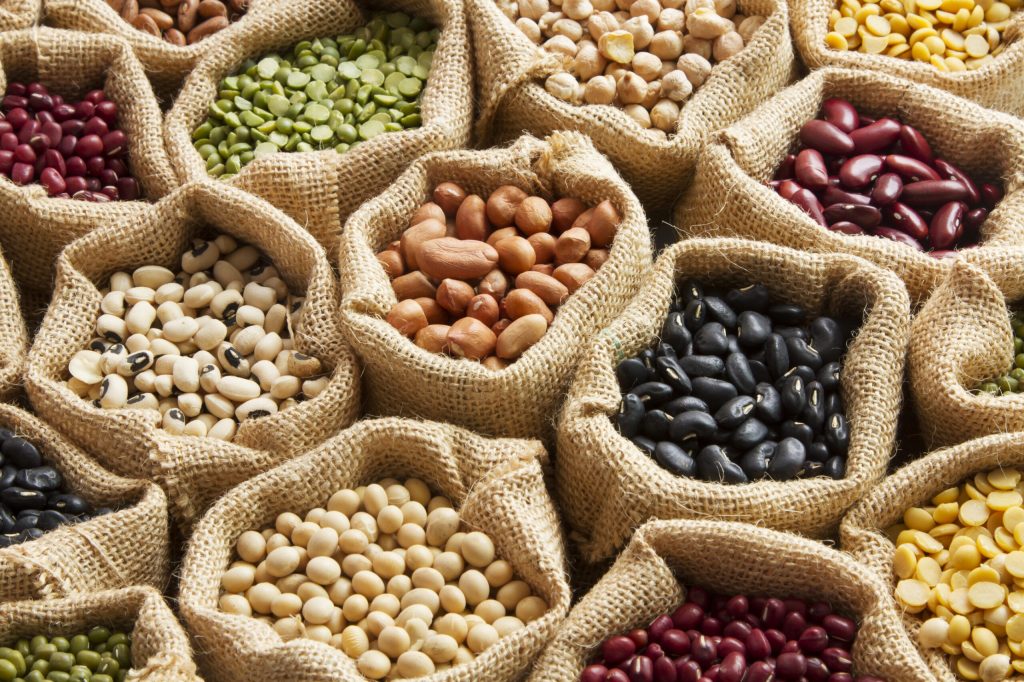
- Lentils
With 18 grams of plant-based protein and 15.6 grams of dietary fiber per cup, lentils are the unsung heroes of the kitchen. They rank high on the antidepressant food scale due to their substantial folate (vitamin B9) content, as low levels of folate are linked to increased risks of depression and dementia. Try adding lentils to salads, omelets, or as a standalone side dish.

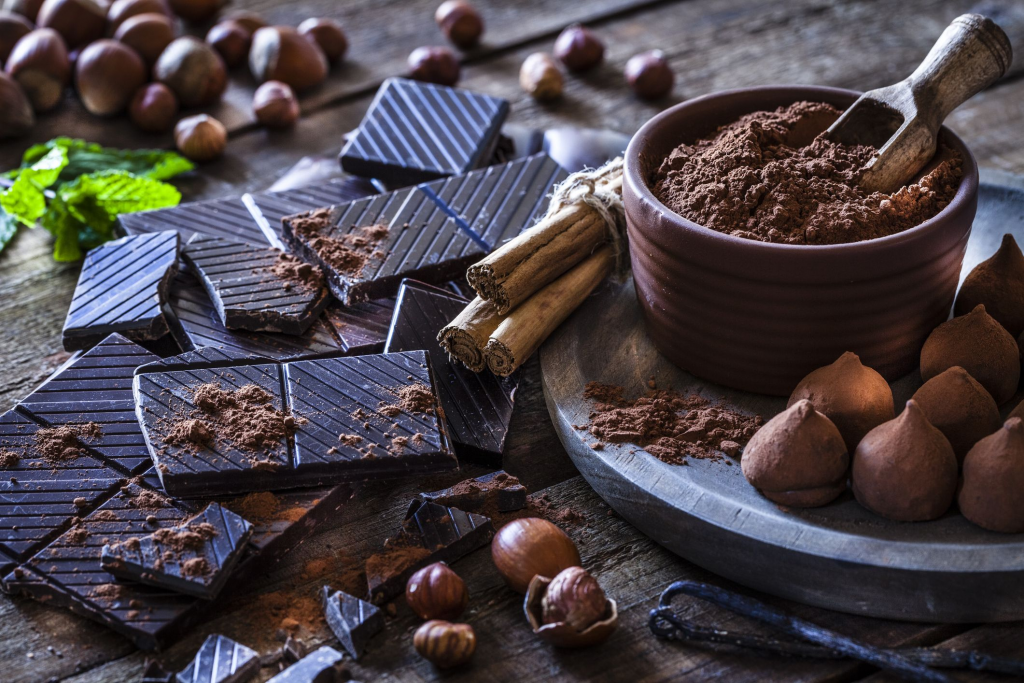
- Dark Chocolate
Despite concerns about lead and cadmium, dark chocolate remains a popular brain-supporting treat. Studies show that consuming responsibly sourced dark chocolate in moderation can benefit cardiovascular health, stabilize blood sugar, and enhance both cerebral blood flow and memory.

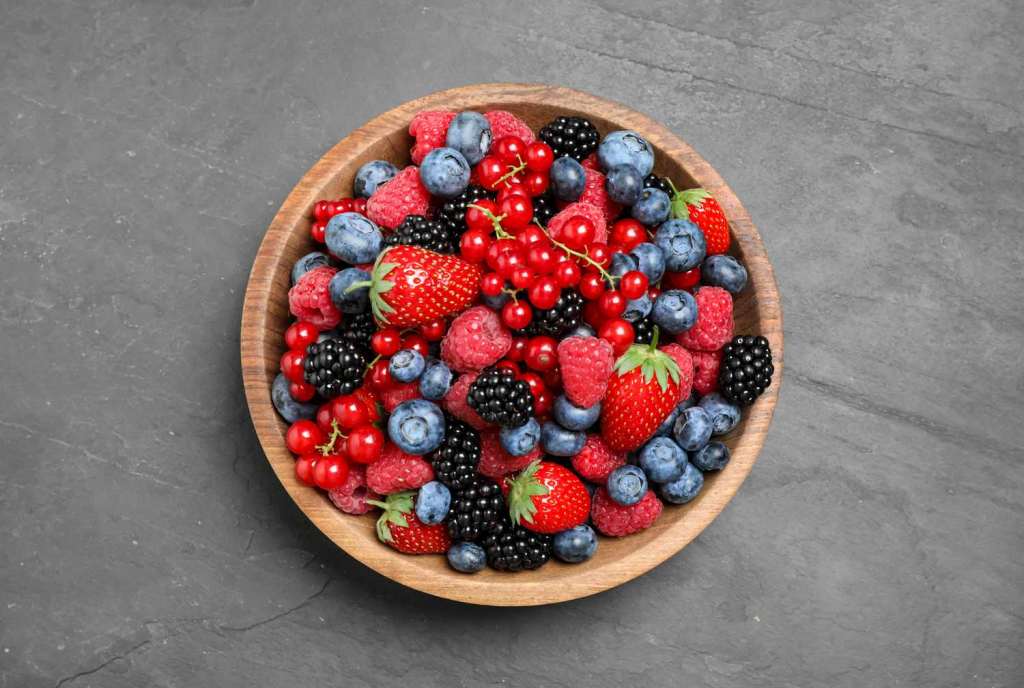
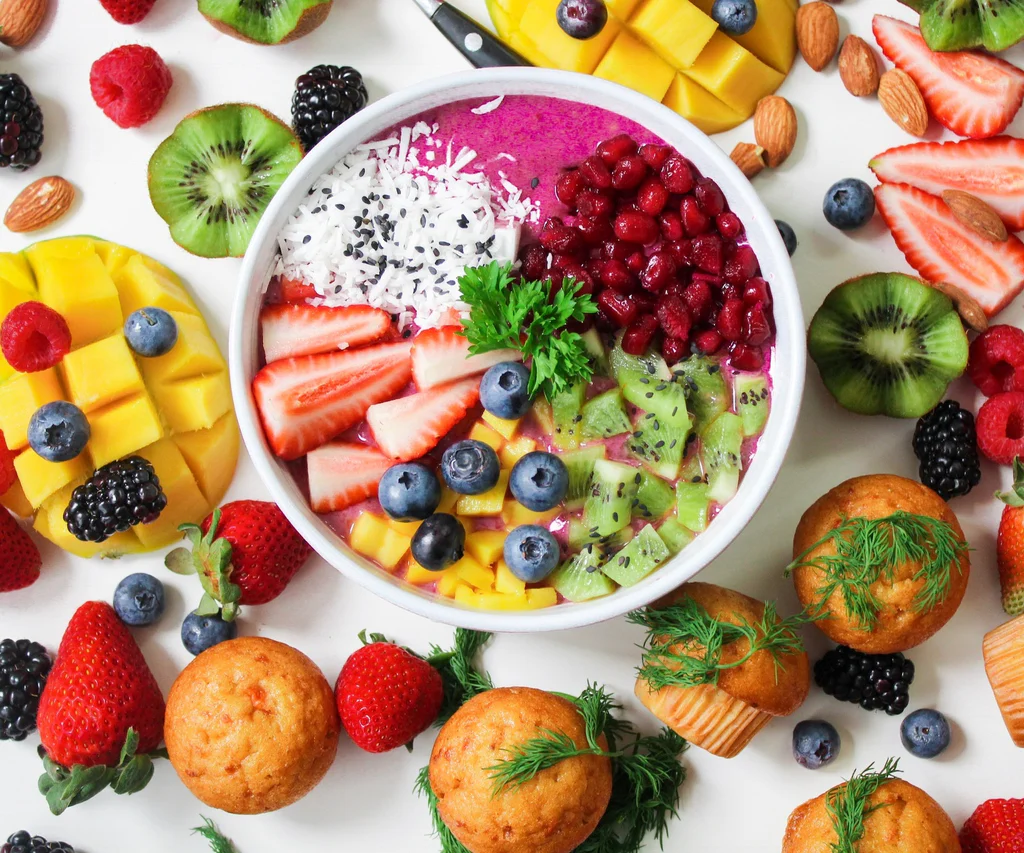
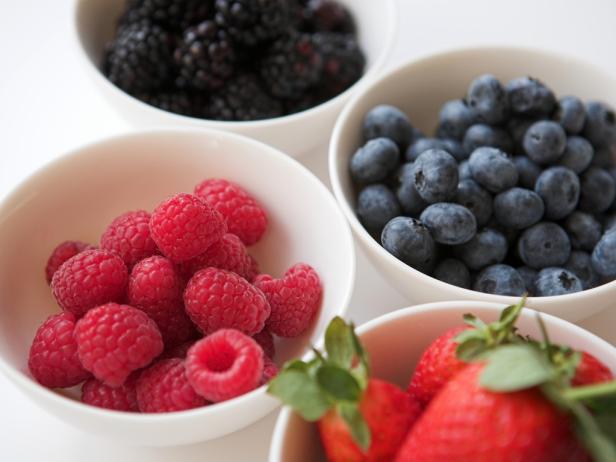
- Berries
Long celebrated for their brain benefits, berries are rich in phytonutrients that support healthy inflammation responses, neurotransmission, and neuroplasticity. Even when out of season, frozen berries retain the same nutritional benefits. Consider adding fiber-rich varieties like raspberries to smoothies, oatmeal, and more.

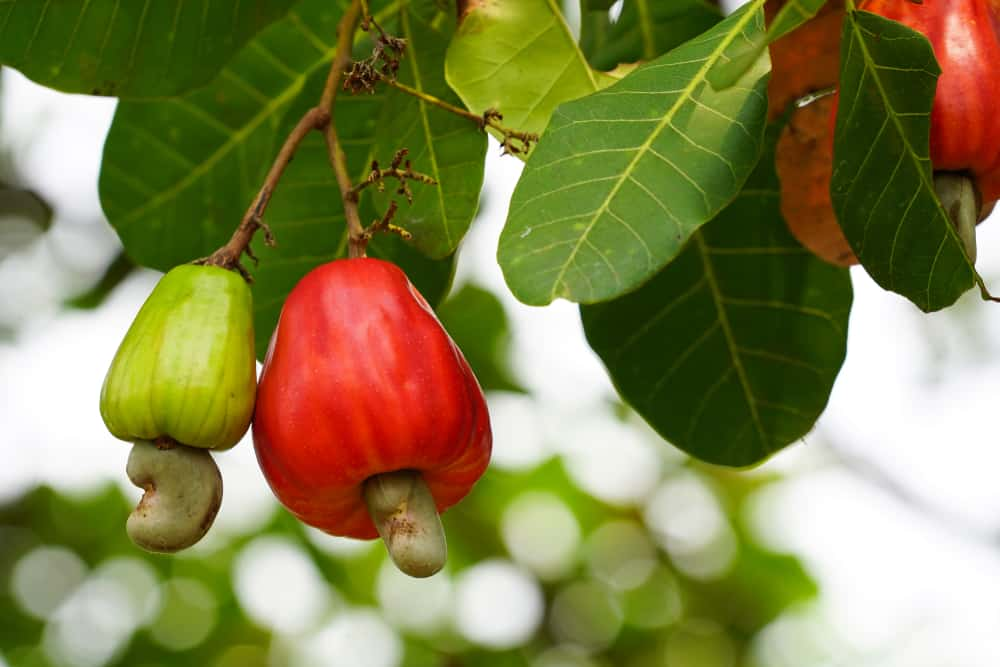
- Cashews
Among various nuts, cashews stand out for their iron content—a vital mineral for brain health, especially important for those on plant-based diets. Cashews are not only delicious with their creamy, sweet profile but also offer high nutritional value.

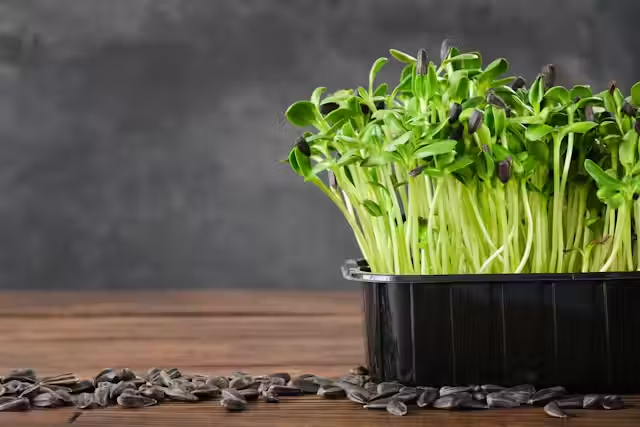
- Microgreens & Sprouts
Microgreens and sprouts are perfect for topping any meal that supports mental health. In nutritional psychiatry, nutrient density is a key principle, and microgreens are a prime example of this. These young plants are packed with minerals and phytonutrients. Growing your own greens and sprouts not only benefits your health but also provides small lessons in mental health. Sprouts give us hope, reminding us that brain cells can continue to grow.

The Takeaway
Incorporating any of these seven nutritious ingredients into your meals can greatly benefit your brain health and mood. The way you prepare these foods is less important than the company you share them with. Nutritional psychiatry reminds us of the power of food to connect us. Eating with loved ones not only promotes mental health but also builds resilience.
























































:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ew_can-soup-upgrade_alt1-960-da25fd0b7abf48149d78b3f6b2f77cc4.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/87305-microwave-popcorn-DDMFS-4x3-b4700cc9b5e440fd9d11eb0bdaf1395f.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Simply-Recipes-Non-Dairy-Coffee-Creamer-LEAD-4-badc00c2ba5546609dbdad45eab97598.jpg)

